-
Table of Contents
“Channeling Efficiency: The Plumbing System’s Journey from Source to Drain!”
Introduction
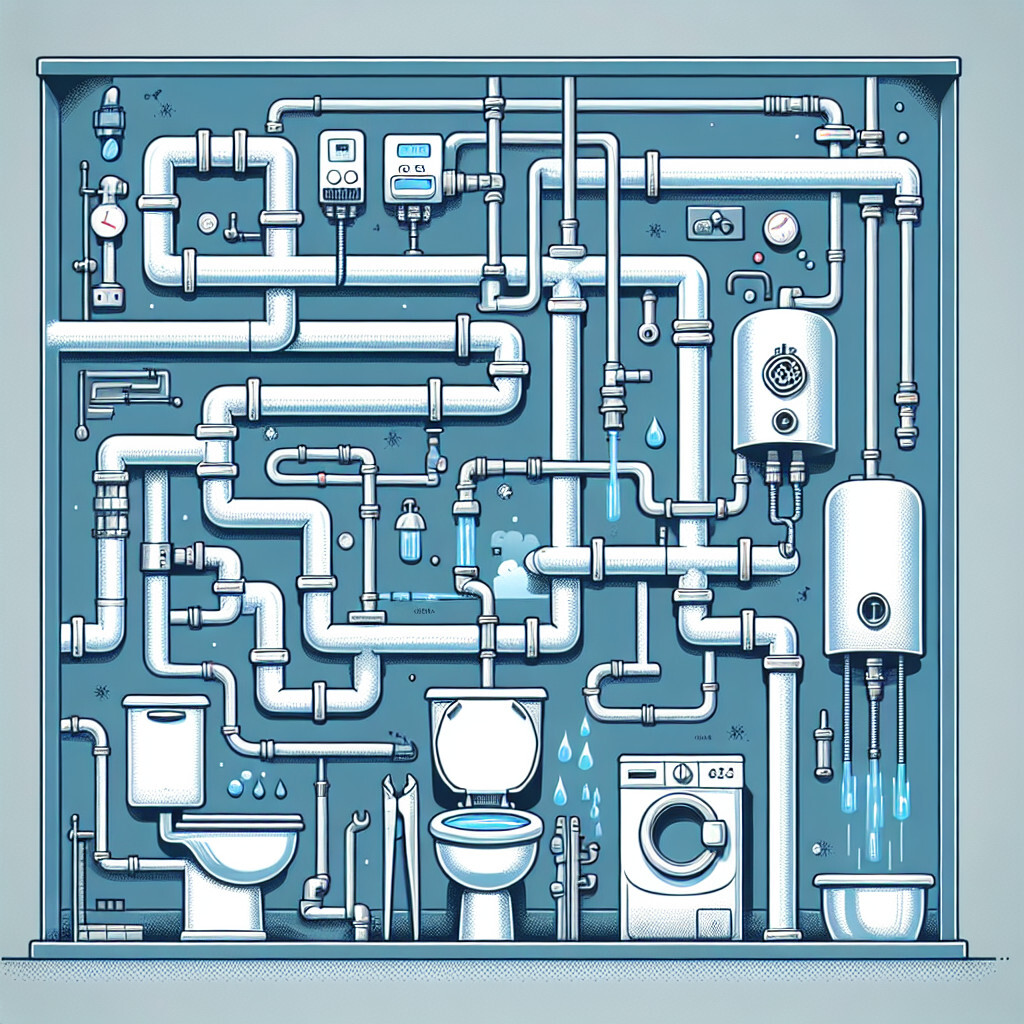
A plumbing system works by providing a means of supply and drainage of water. The system is designed to transport water to various points in a building through a network of pipes, valves, and other fixtures. The supply system operates under pressure to deliver cold and hot water to sinks, tubs, toilets, and appliances. The drainage system, on the other hand, relies on gravity to move waste water and sewage out of the building into the sewer or septic system. Vent pipes are also an integral part of the plumbing system, allowing sewer gases to escape out of the building and providing air so that the waste can flow freely.
Understanding the Basics of Your Home’s Plumbing System
Understanding the basics of your home’s plumbing system is essential for every homeowner. It not only helps in identifying potential problems before they escalate but also aids in making informed decisions when it comes to repairs and maintenance. The plumbing system, though seemingly complex, operates on a few basic principles that are easy to comprehend.
At its core, the plumbing system in your home is a network of pipes, valves, and fixtures that work together to provide clean water for use and remove waste water efficiently. It is a two-part system, comprising the supply system that brings in fresh water, and the drainage system that takes away waste water.
The supply system operates under pressure to ensure that water reaches all parts of your home, from the ground floor to the topmost level. This system is connected to a municipal water supply or a well, depending on your location. The water enters your home through a main supply line, which then branches out to supply individual fixtures like sinks, showers, and toilets. To control the flow of water, each fixture is fitted with a valve. In case of a leak or during repairs, these valves can be turned off to stop the flow of water to that particular fixture without affecting the rest of the system.
The drainage system, on the other hand, relies on gravity to function. It is designed to carry waste water away from your home to a septic tank or a public sewer. This system includes all the drains from your sinks, showers, and toilets, which merge into a single pipe that exits your home. To prevent sewer gases from entering your home, each drain is fitted with a trap, a U-shaped pipe that holds standing water and acts as a seal.
Moreover, the plumbing system also includes a network of vent pipes that allow sewer gases to escape out of your home. These vent pipes extend from the drainage pipes up through the roof of your house. They serve a dual purpose: they allow sewer gases to escape safely, and they also maintain the pressure balance in the drainage system to ensure smooth flow of waste water.
Another crucial component of your home’s plumbing system is the water heater. This appliance heats the water for use in showers, dishwashers, and washing machines. It is connected to the cold-water supply pipe and has its own set of pipes for delivering hot water to the various fixtures in your home.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of your home’s plumbing system can be quite beneficial. It can help you troubleshoot minor issues, understand the cause of a problem when it arises, and communicate effectively with professionals when needed. While the system may seem complex, it operates on simple principles of pressure and gravity. With a basic understanding of these principles and the various components involved, you can gain a better appreciation of the intricate network that works tirelessly to provide clean water and efficient waste disposal in your home.
The Role of Gravity and Pressure in Plumbing Systems
The plumbing system in any building, be it residential or commercial, is a complex network of pipes, valves, and fixtures that work in harmony to provide clean water and dispose of waste. The fundamental principles that govern the operation of these systems are gravity and pressure. Understanding the role of these two forces in plumbing systems can provide a clearer picture of how these systems function and why they are designed the way they are.
Gravity, the force that pulls everything towards the earth, plays a crucial role in the plumbing system. It is primarily responsible for the movement of water and waste through the pipes. For instance, in a typical residential plumbing system, the water supply pipes are installed at a slight angle, not perfectly horizontal. This slight incline allows gravity to assist in moving the water from the source to the various outlets in the home, such as faucets and showerheads. Similarly, gravity is also instrumental in the disposal of waste and wastewater. The drain pipes are designed and installed in such a way that they slope downwards, allowing gravity to pull the waste and wastewater from the building into the sewer system or septic tank.
Pressure, on the other hand, is the force exerted when water is pushed against the walls of the pipes. It is a vital component in the delivery of water throughout a plumbing system. Water pressure is created by the weight of the water itself and any additional pressure applied to move the water. In most municipal water systems, the water is stored in elevated tanks. The height of these tanks creates significant pressure due to the force of gravity acting on the water. This pressure is sufficient to push the water through the network of pipes and into buildings.
In addition to gravity-fed systems, many buildings employ pumps to increase water pressure. This is particularly common in high-rise buildings, where the force of gravity alone is insufficient to deliver water to the upper floors. The pumps work by creating a high-pressure area at the pump outlet, which forces the water through the pipes.
However, while pressure is essential for the operation of a plumbing system, too much pressure can be problematic. Excessive water pressure can lead to leaks, pipe damage, and even the premature failure of appliances and fixtures. Therefore, plumbing systems often include pressure-reducing valves to ensure that the water pressure remains within a safe range.
In conclusion, gravity and pressure are the two fundamental forces that make a plumbing system work. Gravity, with its unyielding pull towards the earth, ensures the smooth flow of water and waste through the system. Pressure, created by the weight of the water and any additional forces applied, ensures that water can be delivered throughout a building, even against the force of gravity. Together, these two forces enable the complex network of pipes, valves, and fixtures that make up a plumbing system to provide clean water and dispose of waste efficiently and effectively. Understanding these principles can provide valuable insight into the design and operation of plumbing systems.
How Does a Plumbing System Maintain Water Supply and Waste Disposal?
A plumbing system is an intricate network of pipes, valves, and fixtures that work in harmony to ensure the smooth flow of water into and out of a building. It is a critical component of any structure, be it residential, commercial, or industrial, as it maintains the water supply and facilitates waste disposal. Understanding how a plumbing system works can provide valuable insights into the maintenance and troubleshooting of common plumbing issues.
The plumbing system operates on simple physics principles, primarily gravity and pressure. The system is divided into two subsystems: the water supply system and the drainage system. The water supply system, as the name suggests, is responsible for bringing fresh water into the building. On the other hand, the drainage system, also known as the DWV (Drain-Waste-Vent), is tasked with removing waste water and sewage out of the building.
The water supply system works under high pressure to allow water to travel upwards into the building. The water is typically sourced from a municipal water supply or a well, and it enters the building through a main supply line. This water is then distributed to various fixtures such as sinks, showers, and toilets through a network of pipes. To ensure that the water remains clean and safe for consumption, it is kept separate from the drainage system.
The drainage system, on the other hand, operates passively, relying on gravity to move waste water and sewage out of the building. The waste from sinks, showers, and toilets flows into larger drain pipes, which eventually lead to the main sewer line. This main sewer line then carries the waste to a sewage treatment facility or a septic tank.
A crucial component of the drainage system is the venting system. Vent pipes, which are connected to the drain pipes, allow sewer gases to escape out of the building, typically through the roof. They also allow air into the drain pipes, which helps waste water and sewage flow smoothly and prevents a vacuum from forming in the pipes.
The plumbing system also includes a series of valves and traps. Valves, such as shut-off valves, allow for the control of water flow, enabling the isolation of certain parts of the system for maintenance or in case of a leak. Traps, on the other hand, are curved sections of pipe located under sinks and other fixtures. They retain a small amount of water after use, forming a seal that prevents sewer gases from entering the building.
In conclusion, a plumbing system is a complex yet efficient system that ensures the continuous supply of clean water and the safe disposal of waste water and sewage. It operates on the principles of pressure and gravity, and includes various components such as pipes, valves, and traps to maintain its functionality. Understanding how a plumbing system works can be beneficial in identifying and addressing common plumbing issues, and can also contribute to more efficient water usage and waste disposal.
The Intricate Workings of a Residential Plumbing System
The intricate workings of a residential plumbing system are a marvel of modern engineering, providing households with a seamless supply of clean water and efficient waste disposal. Understanding the basic principles of how a plumbing system works can be beneficial for homeowners, enabling them to identify potential issues and perform simple maintenance tasks.
A residential plumbing system is essentially a network of pipes, valves, and fixtures that work in harmony to deliver clean water and remove waste. The system is divided into two primary subsystems: the water supply system and the drainage system. These two subsystems operate independently of each other, each serving a distinct purpose.
The water supply system is responsible for delivering fresh water to the household. This subsystem operates under pressure to ensure that water can reach all areas of the home, from the basement to the top floor. The water supply begins at the municipal water main or well, where water is pumped into the home through a water meter that measures usage. This water is then distributed throughout the home via a network of pipes, reaching faucets, showers, toilets, and appliances such as dishwashers and washing machines.
The water supply system also includes a hot water line, which is connected to a water heater. The water heater warms the water to a set temperature before it is distributed to fixtures and appliances that require hot water. Safety devices such as pressure relief valves and temperature and pressure relief valves are installed on water heaters to prevent overheating and excessive pressure build-up.
On the other hand, the drainage system, also known as the DWV (drain-waste-vent) system, is designed to remove waste water and sewage from the home. This subsystem operates based on gravity, with pipes sloping downwards to carry waste and used water away from the home. The DWV system is also responsible for venting sewer gases safely out of the home through vent stacks, which extend through the roof.
The DWV system includes traps, U-shaped pipes that retain a small amount of water, creating a seal to prevent sewer gases from entering the home. These traps are located beneath sinks, showers, and toilets. Moreover, the DWV system also includes cleanouts, which are access points that allow for the removal of blockages.
The two subsystems of a residential plumbing system are designed to work together to provide a safe and sanitary living environment. The water supply system ensures that clean, potable water is readily available for use, while the DWV system efficiently removes waste and prevents harmful gases from entering the home.
In conclusion, the residential plumbing system is a complex yet efficient network that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and comfort of a household. Understanding its basic workings not only demystifies the process but also empowers homeowners to better manage and maintain their plumbing systems. From the pressurized water supply system to the gravity-dependent drainage system, each component plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of the entire system.
Q&A
1. Question: What is the basic principle behind a plumbing system?
Answer: The basic principle behind a plumbing system is gravity. It uses pressure and gravity to transport water and waste. Clean water is supplied under pressure, and waste water is removed by gravity flow.
2. Question: How does water get into a home’s plumbing system?
Answer: Water gets into a home’s plumbing system through a main water supply line that is connected to a municipal water source or a private well. This water is then distributed to different parts of the house through smaller pipes.
3. Question: How does the drainage system in a house work?
Answer: The drainage system in a house works by using gravity. Waste water from sinks, toilets, and showers flows down through the drain pipes and into the sewer system or septic tank. Vent pipes allow sewer gases to escape and provide the necessary air pressure for waste to flow freely.
4. Question: What is the role of a plumbing vent?
Answer: A plumbing vent, also known as a vent stack, helps regulate the air pressure in your plumbing system. It allows fresh air into the plumbing system to help water flow smoothly through the drain pipes. Without a vent, water might not flow out of your house properly and can create a vacuum that could affect the performance of the drains.
Conclusion
A plumbing system works by utilizing a network of pipes, valves, and other components to transport water and waste materials. It operates on the principles of gravity and water pressure. Fresh water is delivered to homes and buildings through pressurized pipes, and is then distributed to various outlets such as faucets and showers. Waste water is removed from the premises through a series of drain pipes that rely on gravity. Vent pipes are also crucial in maintaining the pressure balance and removing sewer gases. Therefore, the plumbing system is a complex yet efficient system that ensures the delivery of clean water and the safe disposal of waste.






